Introduction to Evolution
Imagine the whole world as one big, exciting game of change! Evolution is the process where living things slowly change over time, making over 8.7 million species on Earth.
Imagine the whole world as one big, exciting game of change! Evolution is the process where living things slowly change over time, making over 8.7 million species on Earth.
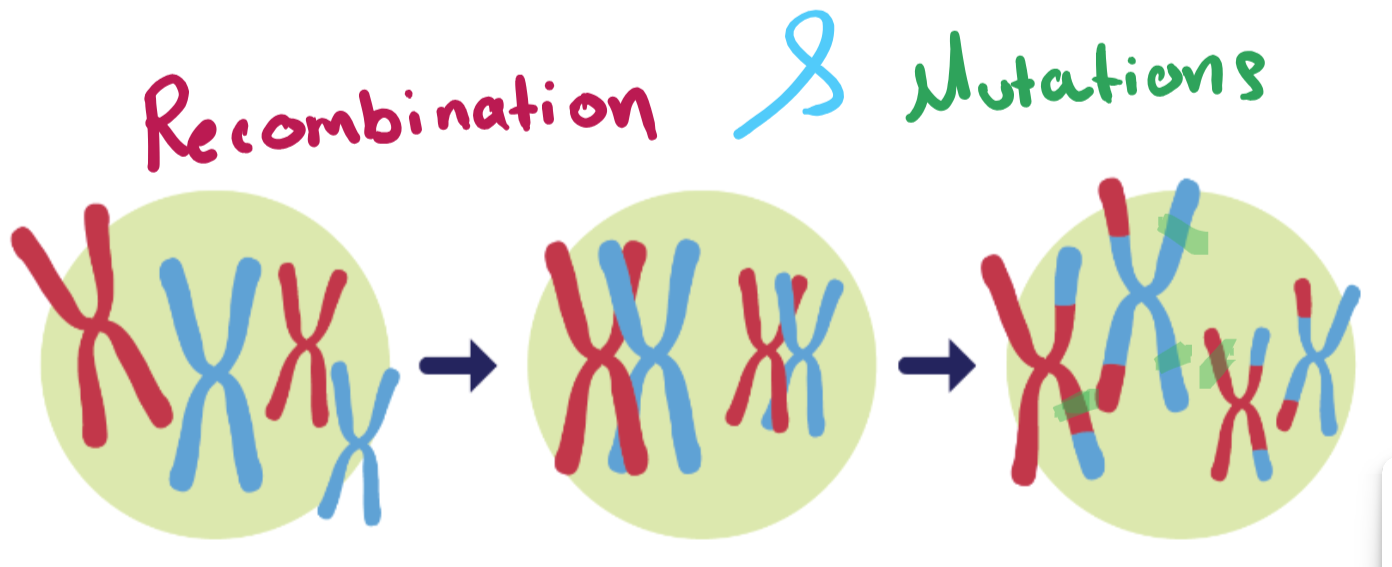
A long, long time ago, life on Earth began with simple RNA strands that evolved into cells, small organisms, fish, then reptiles, and finally into mammals like us!

Scientists can study evolution in many ways, whether that’s looking at animal embryos, tracing the past, or analyzing genes. Let’s explore some of these methods!
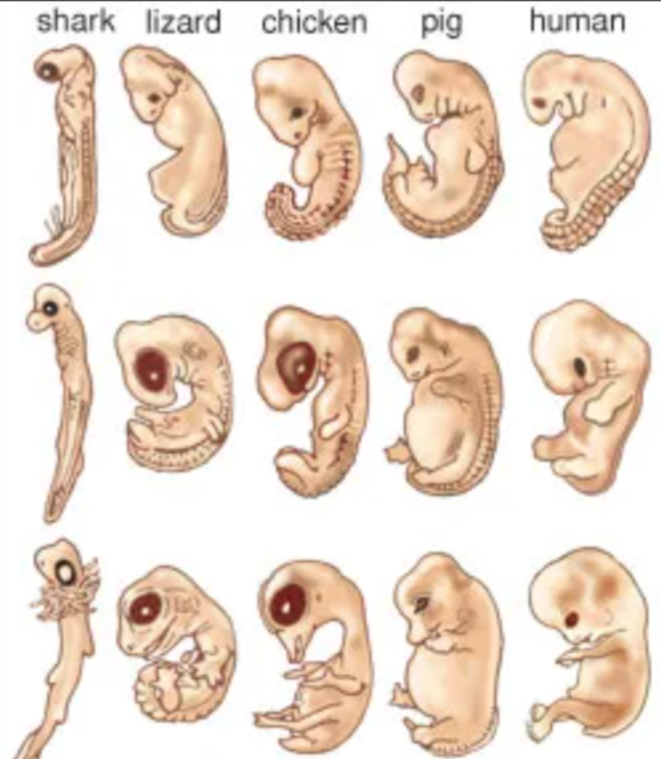
By looking at embryos of different animals, scientists see that all vertebrates (like us) had gill slits and tails at some point, showing we share a common ancestor with fish.
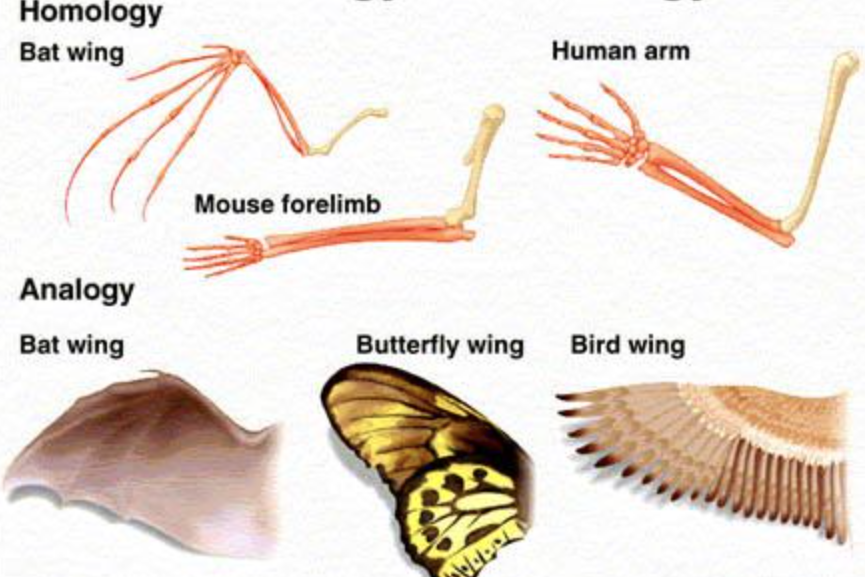
By studying body parts, scientists find:
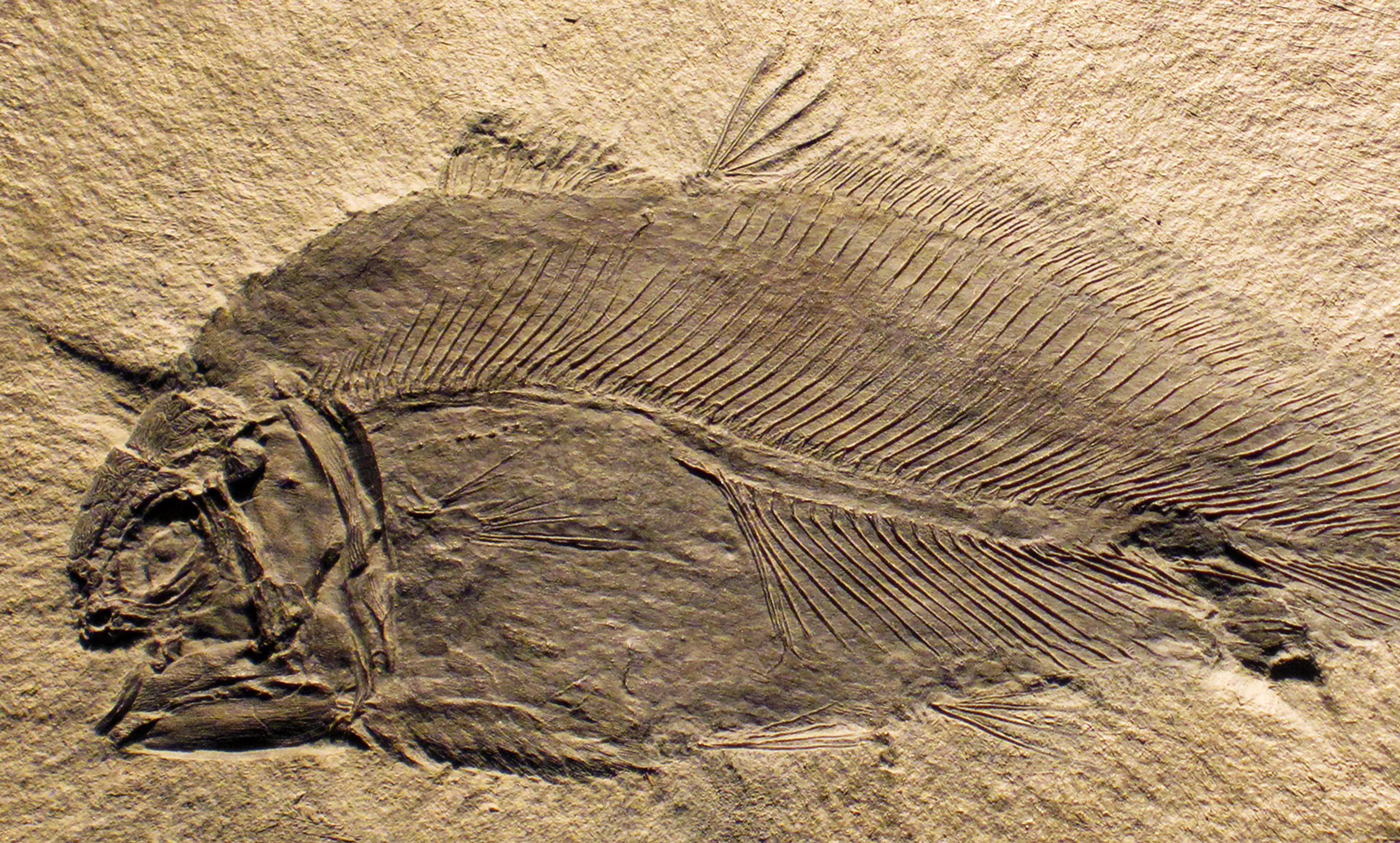
Fossils are like time capsules, showing us what ancient creatures looked like and where they lived. Paleontologists study these to learn about the history of life.

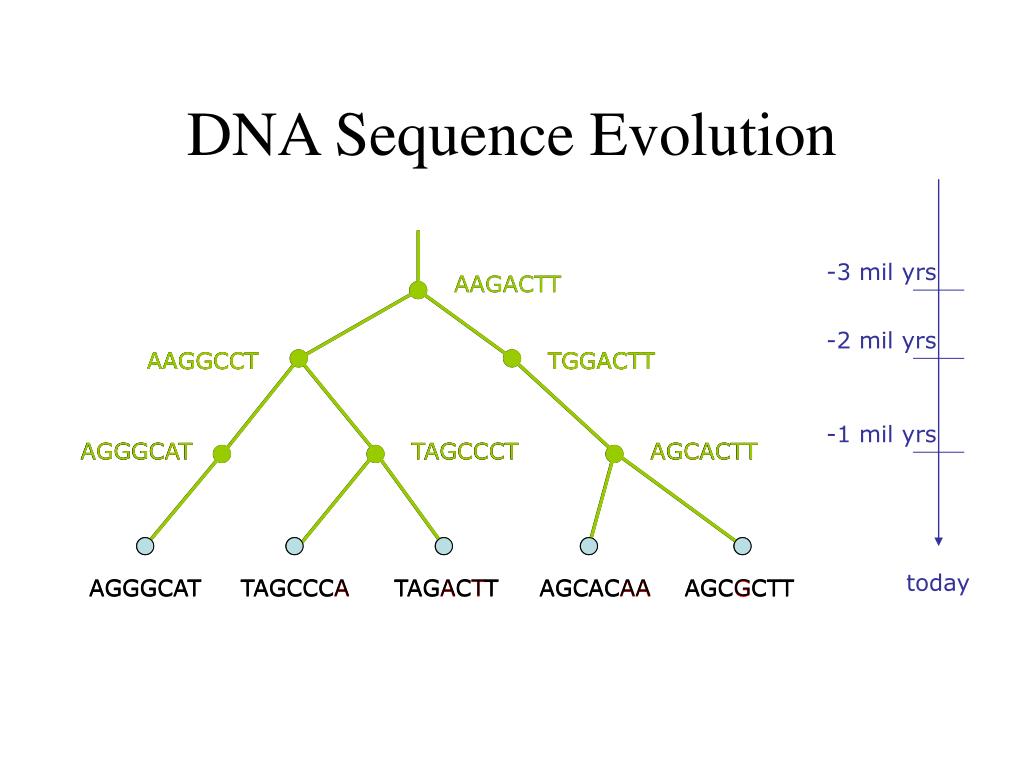
All living things share DNA. By comparing the sequences of nucleotides (the building block of DNA), scientists can figure out how closely related different organisms are.
Evolution shows us how diverse and fascinating life on Earth truly is!
Scientists have recently discovered three new species. Here are snippits of their DNA. Your mission is to identify sequence similarities to discover which two organisms are most closely related. Organism A: TCAGAAGGA Organism B: TCAACAGGC Organism C: AGGGCGAAA Can you complete the mission?
Organism A and B share the most simmilarities in the nucleotide sequence. Their shared DNA leads us to conclude that the organisms are closely related!